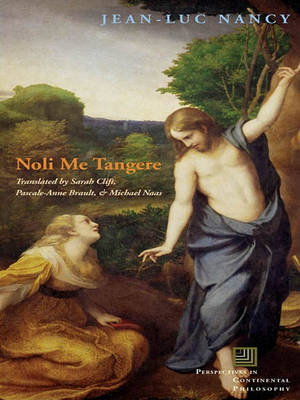Perspectives in Continental Philosophy
6 total works
Written in the wake of Jacques Derrida's death in 2004, Derrida From Now On attempts both to do justice to the memory of Derrida and to demonstrate the continuing significance of his work for contemporary philosophy and literary theory.
If Derrida's thought is to remain relevant for us today, it must be at once understood in its original context and uprooted and transplanted elsewhere. Michael Naas thus begins with an analysis of Derrida's attachment to the French language, to Europe, and to European secular thought, before turning to Derrida's long engagement with the American context and to the ways in which deconstruction allows us to rethink the history, identity, and promise of post-9/11 America.
Taking as its point of departure several of Derrida's later works (from "Faith and Knowledge" and The Work of Mourning to Rogues and Learning to Live Finally), the book demonstrates how Derrida's analyses of the phantasms of sovereignty, the essential autoimmunity of democracy or religion, or the impossible mourning of the nation-state can help us to understand what is happening today in American culture, literature, and politics.
Though Derrida's thought has always lived on only by being translated elsewhere, his disappearance will have driven home this necessity with a new force and an unprecedented urgency. Derrida From Now On is an effect of this force and an attempt to respond to this urgency.
Christian parables have retained their force well beyond the sphere of religion; indeed, they share with much of modern literature their status as a form of address: “Who hath ears to hear, let him hear.” There is no message without there first being—or, more subtly, without there also being in the message itself—an address to a capacity or an aptitude for listening. This is not an exhortation of the kind “Pay attention!” Rather, it is a warning: if you do not understand, the message will go away.
The scene in the Gospel of John in which the newly risen Christ enjoins the Magdalene, “Noli me tangere,” a key moment in the general parable made up of his life, is a particularly good example of this sudden appearance in which a vanishing plays itself out. Resurrected, he speaks, makes an appeal, and leaves.
“Do not touch me.” Beyond the Christ story, this everyday phrase says something important about touching in general. It points to the place where touching must not touch in order to carry out its touch (its art, its tact, its grace).
The title essay of this volume is both a contribution to Nancy’s project of a “deconstruction of Christianity” and an exemplum of his remarkable writings on art, in analyses of “Noli me tangere” paintings by such painters as Rembrandt, Dürer, Titian, Pontormo, Bronzino, and Correggio. It is also in tacit dialogue with Jacques Derrida’s monumental tribute to Nancy’s work in Le toucher—Jean-Luc Nancy.
For the English-language edition, Nancy has added an unpublished essay on the Magdalene and the English translation of “In Heaven and on the Earth,” a remarkable lecture he gave in a series designed to address children between six and twelve years of age. Closely aligned with his entire project of “the deconstruction of Christianity,’” this lecture may give the most accesible account of his ideas about God.
How have we thought "the body"? How can we think it anew? The body of mortal creatures, the body politic, the body of letters and of laws, the "mystical body of Christ"-all these (and others) are incorporated in the word Corpus, the title and topic of Jean-Luc Nancy's masterwork.
Corpus is a work of literary force at once phenomenological, sociological, theological, and philosophical in its multiple orientations and approaches. In thirty-six brief sections, Nancy offers us at once an encyclopedia and a polemical program-reviewing classical takes on the "corpus" from Plato, Aristotle, and Saint Paul to Descartes, Hegel, Husserl, and Freud, while demonstrating that the mutations (technological, biological, and political) of our own culture have given rise to the need for a new understanding of the body. He not only tells the story of this cultural change but also explores the promise and responsibilities that such a new understanding entails.
The long-awaited English translation is a bold, bravura rendering. To the title essay are added five closely related recent pieces-including a commentary by Antonia Birnbaum-dedicated in large part to the legacy of the "mind-body problem" formulated by Descartes and the challenge it poses to rethinking the ancient problems of the corpus. The last and most poignant of these essays is "The Intruder," Nancy's philosophical meditation on his heart transplant. The book also serves as the opening move in Nancy's larger project called "The deconstruction of Christianity."
The End of the World and Other Teachable Moments follows the remarkable itinerary of Jacques Derrida's final seminar, "The Beast and the Sovereign" (2001-3), as the explicit themes of the seminar-namely, sovereignty and the question of the animal-come to be supplemented and interrupted by questions of death, mourning, survival, the archive, and, especially, the end of the world.
The book begins with Derrida's analyses, in the first year of the seminar, of the question of the animal in the context of his other published works on the same subject. It then follows Derrida through the second year of the seminar, presented in Paris from December 2002 to March 2003, as a very different tone begins to make itself heard, one that wavers between melancholy and an extraordinary lucidity with regard to the end. Focusing the entire year on just two works, Daniel Defoe's Robinson Crusoe and Martin Heidegger's seminar of 1929-30, "The Fundamental Concepts of Metaphysics," the seminar comes to be dominated by questions of the end of the world and of an originary violence that at once gives rise to and effaces all things.
The End of the World and Other Teachable Moments follows Derrida as he responds from week to week to these emerging questions, as well as to important events unfolding around him, both world events-the aftermath of 9/11, the American invasion of Iraq-and more personal ones, from the death of Maurice Blanchot to intimations of his own death less than two years away. All this, the book concludes, makes this final seminar an absolutely unique work in Derrida's corpus, one that both speaks of death as the end of the world and itself now testifies to that end-just one, though hardly the least, of its many teachable moments.
Miracle and Machine is a sort of “reader’s guide” to Jacques Derrida’s 1994–95 essay “faith and knowledge,” his most important work on the nature of religion in general and on the unprecedented forms it is taking today through science and the media. It provides essential background for understanding Derrida’s essay, commentary on its unique style and its central figures (e.g., Kant, Hegel, Bergson, and Heidegger), and assessment of its principal philosophical claims about the fundamental duplicity of religion and the ineluctably
autoimmune relationship among religion, science, and the media. Along the way it offers in-depth analysis of Derrida’s treatment of everything from the nature of religious revelation, faith, prayer, sacrifice, testimony, messianicity, fundamentalism, and secularism to the way religion is today being transformed by globalization,
technoscience, and worldwide telecommunications networks.
But Miracle and Machine is much more than a commentary on a single Derrida text. Through references to scores of other works by Derrida, both early and late, it also provides a unique introduction to Derrida’s work in general. It demonstrates that one of the very best ways to understand the terms, themes, claims, strategies, and motivations of Derridean deconstruction from the early 1960s through 2004 is to read critically and patiently, in its spirit and in its letter, an exemplary text such as “Faith and Knowledge.” Finally, Miracle and Machine attempts to put Derrida’s ideas about religion to the test by reading alongside “Faith and Knowledge” an already classic work of American fiction that is more or less contemporaneous with it, Don DeLillo’s 1997 Underworld, a novel that explores the same relationship between faith and knowledge, religion and science, religious revelation and the World Wide Web, messianicity, and weapons of mass destruction—in a word, in two words, miracles and machines.
Class Acts examines two often neglected aspects of Jacques Derrida's work as a philosopher, his public presentations at lectures and conferences and his teaching, along with the question of the "speech act" that links them. What, Michael Naas asks, is one doing when one speaks in public in these ways?
The book follows Derrida's itinerary with regard to speech act theory across three public lectures, from 1971 to 1997, all given, for reasons the book seeks to explain, in Montreal. In these lectures, Derrida elaborated his critique of J. L. Austin and his own subsequent redefinition of speech act theory. The book then gives an overview of Derrida's teaching career and his famous "seminar" presentations, along with his own explicit reflections on pedagogy and educational institutions beginning in the mid-1970s. Naas then shows through a reading of three recently published seminars-on life death, theory and practice, and forgiveness-just how Derrida the teacher interrogated and deployed speech act theory in his seminars. Whether in a conference hall or a classroom, Naas demonstrates, Derrida was always interested in the way spoken or written words might do more than simply communicate some meaning or intent but might give rise to something like an event. Class Acts bears witness to the possibility of such events in Derrida's work as a pedagogue and a public intellectual.