Fortress
5 primary works
Book 6
At the start of the American Civil War (1861), some of the most powerful torts in the country were located in the secessionist states, and many of these fell into Confederate hands. Although a handful of key sites remained in the Union, the remainder had to be won back through bombardment or assault. Forts such as Fort Sumter, Fort Morgan and Fort Pulaski formed the centerpiece in the struggle for control of the Confederate coastline. This book examines the stone forts that played a crucial part in the course of the Civil War, covering their design, construction, and the way they were armed and manned.
Book 50
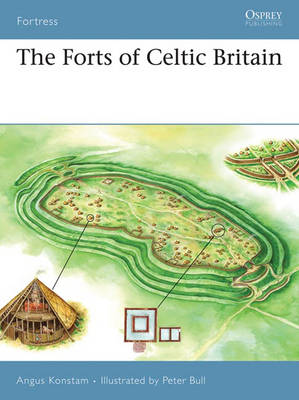
Half a millennium before the Romans first arrived in Britain an even more ferocious people, the Celts, arrived in what is now south-eastern England. The Celts remained in Britain long after the Romans departed, and although driven into the remoter corners of the island by English invaders the people who remained clung onto their Celtic heritage, and defended their remaining lands against all-comers. In order to defend their lands from other tribes or outside invaders, these people established powerful fortified sites that served as places of refuge in wartime and as administrative and trading centres in times of peace. This book examines these fascinating forts, which varied considerably from the mysterious brochs and duns found in northern Britain, to the hill-top forts ranging in size, to the promontory forts that formed powerful coastal strongholds all around the island's shores.
Book 80
When the Romans left Britain around AD 410, the unconquered native peoples of modern Scotland, Ireland and Wales were presented with the opportunity to pillage what remained of Roman Britain. The Post-Roman Britons did their best to defend themselves by using fortifications. While some Roman forts were maintained, the Post-Roman Britons also created new strongholds, or re-occupied some of the hill-forts first built by their ancestors. The most famous warlord of the 'Dark Ages' was the legendary Arthur. His attempt to unite the Britons in the face of Saxon invaders was doomed, and in a little over two centuries the country had become Saxon England. However, for a few brief decades, 'Arthur of the Britons' did what he could to safeguard the culture and civilisation of Post-Roman Celtic Britain.
Book 85
A strategically important natural harbor in the Orkney Islands, Scapa Flow served as Britain's main fleet anchorage during World Wars I and II. In 1914 and again in 1939, the British began building a comprehensive defensive network by fortifying the entrances to Scapa Flow, and then extended these defenses to cover most of Orkney. By 1940, it had become an island fortress, the largest integrated defensive network of its kind in Europe, manned by as many as 50,000 Commonwealth troops.
Book 92
This concise guide actually covers not just Pictish fortifications, but all those in use in early medieval Scotland, including those of Strathclyde and Rheged and of the Dal Riata. Konstam introduces the reader to the principal types of fort, including the re-use of earlier defences, before offering more in-depth surveys of Dundurn and Dunadd. As well as architecture and construction he looks at the use of the forts in war and peace, to control the landscape and act as royal strong points.