The Springer International Series in Engineering and Computer Science
4 primary works
Book 121
Real-Time UNIX® Systems
by Borko Furht, Dan Grostick, David Gluch, Guy Rabbat, John Parker, and Meg McRoberts
Published 31 December 1990
A growing concern of mine has been the unrealistic expectations for new computer-related technologies introduced into all kinds of organizations. Unrealistic expectations lead to disappointment, and a schizophrenic approach to the introduction of new technologies. The UNIX and real-time UNIX operating system technologies are major examples of emerging technologies with great potential benefits but unrealistic expectations. Users want to use UNIX as a common operating system throughout large segments of their organizations. A common operating system would decrease software costs by helping to provide portability and interoperability between computer systems in today's multivendor environments. Users would be able to more easily purchase new equipment and technologies and cost-effectively reuse their applications. And they could more easily connect heterogeneous equipment in different departments without having to constantly write and rewrite interfaces. On the other hand, many users in various organizations do not understand the ramifications of general-purpose versus real-time UNIX. Users tend to think of "real-time" as a way to handle exotic heart-monitoring or robotics systems. Then these users use UNIX for transaction processing and office applications and complain about its performance, robustness, and reliability. Unfortunately, the users don't realize that real-time capabilities added to UNIX can provide better performance, robustness and reliability for these non-real-time applications. Many other vendors and users do realize this, however. There are indications even now that general-purpose UNIX will go away as a separate entity. It will be replaced by a real-time UNIX. General-purpose UNIX will exist only as a subset of real-time UNIX.
Book 326
Video and Image Processing in Multimedia Systems
by Borko Furht, Stephen W. Smoliar, and HongJiang Zhang
Published 31 October 1995
Video and Image Processing in Multimedia Systems treats a number of critical topics in multimedia systems, with respect to image and video processing techniques and their implementations. These techniques include:
This book serves as an invaluable reference with respect to the most important standards in the field. Video and Image Processing in Multimedia Systems is suitable as a textbook for course use.
- Image and video compression techniques and standards, and
- Image and video indexing and retrieval techniques.
This book serves as an invaluable reference with respect to the most important standards in the field. Video and Image Processing in Multimedia Systems is suitable as a textbook for course use.
Book 376
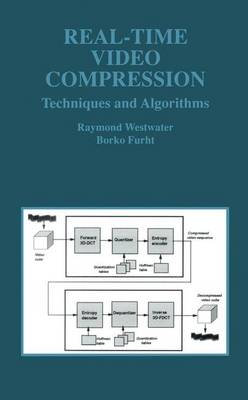
Real-Time Video Compression: Techniques and Algorithms introduces the XYZ video compression technique, which operates in three dimensions, eliminating the overhead of motion estimation. First, video compression standards, MPEG and H.261/H.263, are described. They both use asymmetric compression algorithms, based on motion estimation. Their encoders are much more complex than decoders. The XYZ technique uses a symmetric algorithm, based on the Three-Dimensional Discrete Cosine Transform (3D-DCT). 3D-DCT was originally suggested for compression about twenty years ago; however, at that time the computational complexity of the algorithm was too high, it required large buffer memory, and was not as effective as motion estimation. We have resurrected the 3D-DCT-based video compression algorithm by developing several enhancements to the original algorithm. These enhancements make the algorithm feasible for real-time video compression in applications such as video-on-demand, interactive multimedia, and videoconferencing. The demonstrated results, presented in this book, suggest that the XYZ video compression technique is not only a fast algorithm, but also provides superior compression ratios and high quality of the video compared to existing standard techniques, such as MPEG and H.261/H.263. The elegance of the XYZ technique is in its simplicity, which leads to inexpensive VLSI implementation of any XYZ codec.
Real-Time Video Compression: Techniques and Algorithms can be used as a text for graduate students and researchers working in the area of real-time video compression. In addition, the book serves as an essential reference for professionals in the field.
Real-Time Video Compression: Techniques and Algorithms can be used as a text for graduate students and researchers working in the area of real-time video compression. In addition, the book serves as an essential reference for professionals in the field.
Book 379
Motion Estimation Algorithms for Video Compression
by Borko Furht, Joshua Greenberg, and Raymond Westwater
Published 30 November 1996
Video technology promises to be the key for the transmission of motion video. A number of video compression techniques and standards have been introduced in the past few years, particularly the MPEG-1 and MPEG-2 for interactive multimedia and for digital NTSC and HDTV applications, and H.2611H.263 for video telecommunications. These techniques use motion estimation techniques to reduce the amount of data that is stored and transmitted for each frame. This book is about these motion estimation algorithms, their complexity, implementations, advantages, and drawbacks. First, we present an overview of video compression techniques with an emphasis to techniques that use motion estimation, such as MPEG and H.2611H.263. Then, we give a survey of current motion estimation search algorithms, including the exhaustive search and a number of fast search algorithms. An evaluation of current search algorithms, based on a number of experiments on several test video sequences, is presented as well. The theoretical framework for a new fast search algorithm, Densely-Centered Uniform-P Search (DCUPS), is developed and presented in the book. The complexity of the DCUPS algorithm is comparable to other popular motion estimation techniques, however the algorithm shows superior results in terms of compression ratios and video qUality. We should stress out that these new results, presented in Chapters 4 and 5, have been developed by Joshua Greenberg, as part of his M.Sc. thesis entitled "Densely-Centered Uniform P-Search: A Fast Motion Estimation Algorithm" (FAU, 1996).